Genetics and cell biology of cancer: T-cell lymphoblastic neoplasms
Research summary:
T-cell lymphoblastic leukaemia/lymphoma is a haematological disease with an urgent need for reliable prognostic biomarkers that allow therapeutic stratification and dose adjustment. Therefore, the major aim of our work is to decipher new molecular biomarkers and to propose more effective and less toxic treatments. To this end, we are using mouse models and human samples to integrate data from genomics and transcriptomics approaches as a start point to identify new driver-molecular mechanisms. In the last years we have demonstrated the overexpression of critical oncogenes in these neoplasms (such as c-MYC, ABL1, BCR-ABL and SMO) due to the combinatorial effect of down-regulated microRNAs, as well as the inactivation of tumour suppressor genes by allele deletion and epigenetic events (CDKN2A, CDKN2B and EPHA7). Our data revealed a considerable degree of intratumoral heterogeneity helped by the existence of RNA editing. Among the most recent contributions, we have demonstrated that the simultaneous deregulation of CDKN1C, E2F1 and TP53 genes by epigenetic mechanisms and/or the deregulation of specific microRNAs might be useful to predict tumour aggressiveness. Taking advantage of exome analyses and the versatility of RNA-Seq, we have identified new mutations and significant changes in gene expression, which served to propose new directed therapies in the context of a personalized precision medicine. Our results highlight the potential of RNA-Seq to identify new cryptic fusions, which could be drivers or tumour-maintaining passenger genes. Our data have also revealed that down regulation of different combinations of isoforms of the tumour suppressor FBXW7 is a sine qua non condition to induce a proliferative pattern in a cell model system. In addition, we have demonstrated that FADD phosphorylation may serve as a predictor for T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma aggressiveness and clinical status. Finally, we have shown that reducing the aconitase activity with fluorocitrate decreases the viability of T-cell lymphoblastic neoplasia cells in correlation to the differential ACO1 expression. These findings were confirmed in vivo on athymic nude-mice by using tumour xenografts derived from tumour T-cell lines expressing different levels of ACO1. We are currently interested in evaluating the involvement of RNA editing, exosome traffic and deregulation of long and short ncRNAs to achieve a comprehensive view of the complex regulatory networks deregulated in these neoplasms. Our translational dimension was strengthened by our incorporation to the CIBERER Consortium and to the Institute for Health Research Foundation Jiménez Diaz.
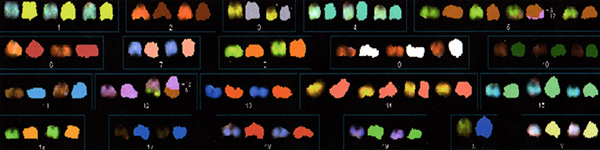
Figure 1. Abnormal spectral karyotype of a sample of murine T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma.
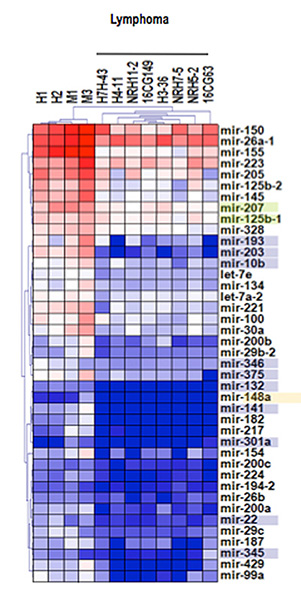
Figure 2. Transcriptomic profiles of miRNA expression in murine T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma.
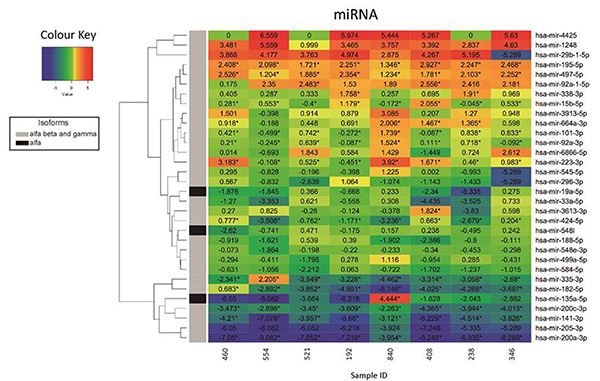
Figure 3. Heatmap representation depicting the expression changes of selected microRNAs in tumour samples as determined by small-RNA-seq analysis.
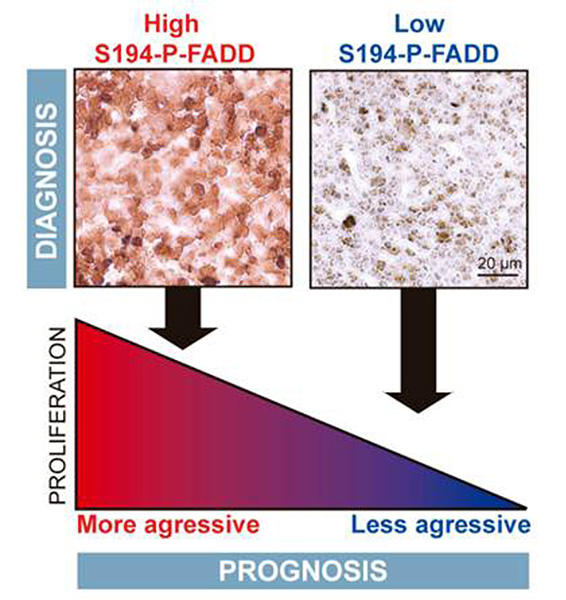
Figure 4. Proposed model of association between FADD phosphorylation and prognosis of T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma.
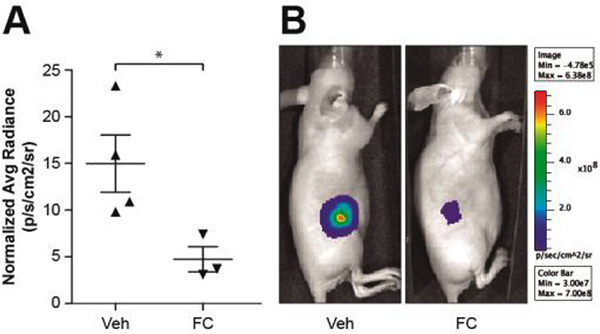
Figure 5. Effect of fluorocitrate on tumour xenografts generated with a human cell line derived from T-cell lymphoblastic neoplasia.

| Last name | Name | Laboratory | Ext.* | Professional category | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blázquez Castro | Alfonso | 327 | 4653 | Tco. de Investigación y Laboratorio | |
| Cobos Fernández | Mª Angeles | 327 | 4653 | macobos(at)cbm.csic.es | Titulado Superior Grado de Doctor |
| González Vasconcellos | Iria | 327 | 4653 | iria.gonzalez(at)cbm.csic.es | Titulado Sup.de Actividades Técn. y Profes. GP1 |
| Lahera Alonso | Antonio | 327 | 4653 | a.lahera(at)cbm.csic.es | Tit.Sup.Activ.Técn.y Profes. GP1 |
| López Nieva | María del Pilar | 327 | 4653 | pilar.lopez(at)cbm.csic.es | Contratado CIBER |
| Ruiz García | Sara | 327 | 4653 | s.garcia@cbm.csic.es | Tit.Sup.Activ.Técn.y Profes. GP1 |
| Santos Hernández | Javier | 327 | 4627/4653 | jsantos(at)cbm.csic.es | Catedrático Universidad, GA |
| Vela Martín | Laura | 327 | 4653 | Tco. de Investigación y Laboratorio | |
| Vaquero Lorenzo | Concepción | 327 | 4653 | cvaquero(at)cbm.csic.es | Titulado Sup.de Actividades Técn. y Profes. GP1 |
| Villa Morales | María Consuelo | 327 | 4653 | mvilla(at)cbm.csic.es | Profesor Contratado Universidad, GA |
Relevant publications:
- Pilar López-Nieva, Pablo Fernández-Navarro, Osvaldo Graña-Castro, Eduardo Andrés-León, Javier Santos, María Villa-Morales, María Ángeles Cobos-Fernández, Laura González-Sánchez, Marcos Malumbres, María Salazar-Roa, and José Fernández-Piqueras. Detection of novel fusion-transcripts by RNA-Seq in T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma. Scientific Reports (2019) 9 (1) : 5179 doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41675-3.
- Laura Gonzalez-Sanchez, Maria Á. Cobos-Fernandez, Pilar Lopez-Nieva, Maria Villa-Morales, K Stamatakis, Jose M. Cuezva, Jose L. Marin Rubio, Irene Vazquez-Dominguez, Iria Gonzalez-Vasconcellos, Eduardo Salido, Pilar Llamas, Jose L. Lopez-Lorenzo, J Santos and Jose Fernandez-Piqueras*. TITULO: Exploiting the passenger ACO1-deficiency arising from 9p21 deletions to kill T-cell lymphoblastic neoplasia cells. Carcinogenesis. 2019 Nov 17. pii: bgz185. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgz185.
- Vázquez-Domínguez, I., González-Sánchez, L., López-Nieva, P., Villa-Morales, M., Cobos- Fernández, M.A., Sastre, I., Fraga, M.F., Fernández, A. F., Malumbres, M., Salazar-Roa, M., Graña-Castro, O., Santos, J., Llamas, P., López-Lorenzo, J.L. and Fernández-Piqueras, J. Downregulation of specific FBXW7 isoforms with differential effects in T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma. Oncogene (2018) doi: 10.1038/s41388-019-0746-1.
- Marín-Rubio, J.L,. Pérez-Gómez, E., Fernández-Piqueras, J. and Villa-Morales, M. S194-P-FADD as a marker of aggressiveness and poor prognosis in human T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma. Carcinogenesis (2018) pii: bgz041. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgz041
- Roncero AM, López-Nieva P, Cobos-Fernández MA, Villa-Morales M, González-Sánchez L, López-Lorenzo JL, Llamas P, Ayuso C, Rodríguez-Pinilla SM, Arriba MC, Piris MA, Fernández-Navarro P, Fernández AF, Fraga MF, Santos J, Fernández-Piqueras J. Contribution of JAK2 to T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma. REVISTA: Leukemia (2016) Jan;30(1):94-103. doi: 10.1038/leu.2015.202.
- Eduardo Pérez-Gómez, Clara Andradas, María M. Caffarel, Sandra Blasco-Benito, Elena García-Taboada, María Villa-Morales, Estefanía Moreno, Sigrid Hamann, Juana M. Flores, Ester Martín, Antonia Wenners, Ibrahim Alkatout, Wolfram Klapper, Maret Bauer, Norbert Arnold, Joaquín Soriano, Manuel Pérez, Diego Megías, Gema Moreno-Bueno, Silvia Ortega-Gutiérrez, Marta Artola, Henar Vázquez-Villa, Miguel Quintanilla, José Fernández-Piqueras, Enric I. Canela, Peter J. McCormick, Manuel Guzmán and Cristina Sánchez. Cannabinoid receptor CB2 is a pivotal regulator of HER2 oncogenic signaling in breast cáncer. REVISTA J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015 Apr 8;107(6). pii: djv077. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djv077.
- Bueno MJ, Gómez de Cedrón M, Pérez de Castro I, Gómez-López G, Di Lisio L, Montes Moreno S, Martínez N, Guerrero M, Sánchez-Martínez R, Santos J, Pisano, DG, Piris MA, Fernández-Piqueras J and Malumbres M (2011) Combinatorial effects of microRNAs to suppress the Myc oncogenic pathway. Blood 117(23): 6255-66.
- Bueno MJ, Gómez de Cedrón M, Laresgoiti U, Fernández-Piqueras J, Zubiaga A and Malumbres M (2010) Multiple E2F-induced microRNAs prevent replicative stress in response to mitogenic signalling. Molecular Cellular Biology 30 (12): 2983-2995.
- Santos J, González-Sánchez L, Matabuena-de Yzaguirre M, Villa-Morales M, Cozar P, López-Nieva P, Fernández-Navarro P, Fresno M, Díaz MD, Guenet JL, Montagutelli X & Fernández-Piqueras J. (2009) A role for stroma-derived Annexin A1 as mediator in the control of genetic susceptibility to T-cell lymphoblastic malignancies through PGE2 secretion. Cancer Res 69(6): 2577-87.
- Bueno MJ, Pérez de Castro I, Gómez de Cedrón M, Santos J, Calin GA, Cigudosa JC, Croce CM, Fernandez-Piqueras J, Malumbres M (2008) Genetic and epigenetic silencing of microRNA-203 enhances ABL1 and BCR-ABL1 oncogene expression. Cancer Cell, 13: 496-506.




















