Physiopathological aspects of glycine transporters in glycinergic neurotransmission: hyperekplexia and pain
Research summary:
The group is dedicated to the study of Na+-and Cl--dependent glycine transporters (GlyTs), which are essential modulators of the glycine-mediated neurotransmission in the Central Nervous System. We study the physiology and pathologies associated to the glycinergic transmission such as hyperekplexia and pain. Hyperekplexia is a rare sensorimotor disorder provoked by the interruption of the glycinergic inhibition that may have severe consequences in neonates. The neuronal glycine transporter GlyT2, which removes and recycles synaptic glycine to supply neurotransmitter for synaptic vesicle refilling, is nonfunctional in the presynaptic defect causing the disease. Our aim is to identify and analyze the pathogenic mechanisms of novel or known mutations in the human GlyT2 gene (SLC6A5) found in hyperekplexia patients. The effects of the mutations on the three-dimensional structure, biogenesis, intracellular trafficking, oligomerization, interactoma and, eventually, the function of the transporter are our research objectives. We have generated and validated 3D models of GlyTs structure based on the first crystalized eukaryotic homologue. By functional assays in cells and proteoliposomes, we have classified the 30 mutations known so far and identified folding-deficient mutants that are amenable to rescue by chemical chaperones. We have localized small molecules and regions in the transporter structure that modulate folding, trafficking and activity. This will allow developing specific pharmacopherones as candidate therapeutic tools for hyperekplexia.
By combination of in silico and experimental data obtained by biochemical and electrophysiological analysis of mutants in cell lines and Xenopus laevis oocytes, we found the location of the third sodium site in GlyT2 which remained unknown, and we described a specific allosteric coupling of this site and the chloride binding-site. This new information will be translated to GlyT2 hyperekplexia-associated mutants.
An additional aspect of our research is focused to the role of GlyTs in pain perception. GlyT2 plays a key role in the modulation of the nociceptive signal in spinal cord interneurons. We demonstrated that pain signaling compounds and agonists of pro-nociceptive P2X receptors up-regulate GlyT2 plasma membrane expression and transport. We showed that P2X2 and P2X3 receptor activation impacts glycinergic neurotransmission in spinal cord primary neurons and modulates GlyT2. Hence, spontaneous glycinergic currents measured by patch clamp, were modulated concurrently with the glycine release and the uptake by GlyT2 in response to P2X receptor agonists. Our data suggest the fine tuning of GlyT2 affects nociceptive signal conduction and encourage us to explore possible modulators of its activity applicable to analgesia.
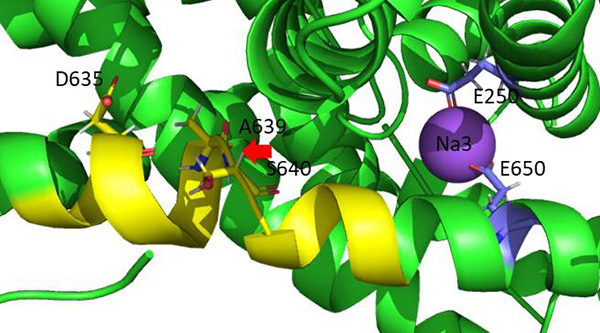
Figure 1. Isoform-specific allosteric properties of transmembrane domain 10 in GlyT2 connect Na3 site with chloride-binding site.
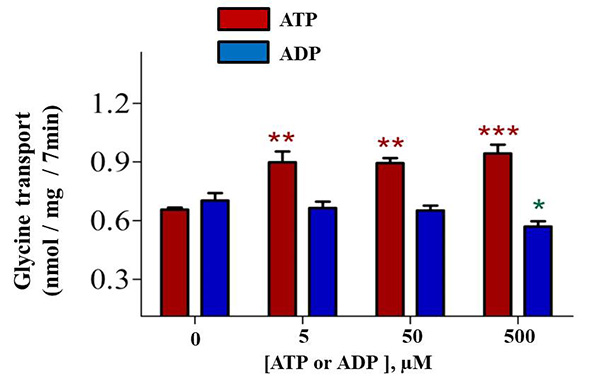
Figure 2. GlyT2 transport activity is differentially modulated by the action of P2X and P2Y receptors.

| Last name | Name | Laboratory | Ext.* | Professional category | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| López Corcuera | Beatriz | 304 | 4631 | blopez(at)cbm.csic.es | Catedrático Universidad, GA |
| Morales González | Beatriz | 304 | 4656 | Estudiante TFG | |
| Sarmiento Jiménez | Jorge | 304 | 4656 | jsarmiento(at)cbm.csic.es | Investigador |
Relevant publications:
- de la Rocha-Muñoz A, Núñez E, Vishwanath AA, Gómez-López S, Dhanasobhon D, Rebola N, López-Corcuera B, de Juan-Sanz J, Aragón C. "The presynaptic glycine transporter GlyT2 is regulated by the Hedgehog pathway in vitro and in vivo". Commun Biol. 2021 Oct 18;4(1):1197. DOI: 10.1038/s42003-021-02718-6. PMID: 34663888.
- Benito-Muñoz, C., Perona, A., Felipe, R., Pérez-Siles, G., Núñez, E., Aragón, C. and López-Corcuera, B. Structural determinants of the glycine transporter 2 (GlyT2) for the selective inhibitors ALX1393 and ORG25543. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021 May 18. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00602. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 34003005.
- Danbolt, N.C., López-Corcuera, B. & Zhou, Y. Reconstitution of GABA, Glycine and Glutamate Transporters. Neurochem Res (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03331-z.
- de la Rocha-Muñoz, A., Melgarejo, E., Aragón, C and López-Corcuera, B. Rescue of two trafficking-defective variants of the neuronal glycine transporter GlyT2 associated to hyperekplexia. Neuropharmacology. 2021 Mar 29;189:108543. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108543.
- Jiménez#, E., Fornés#, A., Felipe, R., Núñez, E., Aragón, C. and López-Corcuera, B. Calcium-dependent regulation of the neuronal glycine transporter GlyT2 by M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Neurochem Res. 2021. doi: 10.1007/s11064-021-03298-x.
- da Silva VD, Silva RR, Neto JG, López-Corcuera B, Guimarães MZ, Noël F, Buarque CD. New α-hydroxy-1,2,3-triazoles and 9H-fluorenes-1,2,3-triazoles: synthesis and evaluation as Glycine Transporter 1 Inhibitors. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 31(6): 1258-1269, 2020.
- de la Rocha-Muñoz A, Núñez E, Arribas-González E, López-Corcuera B, Aragón C, de Juan-Sanz J. “E3 ubiquitin ligases LNX1 and LNX2 are major regulators of the presynaptic glycine transporter GlyT2”. Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 18;9(1):14944. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-51301-x.
- López-Corcuera, B., Arribas-González, E. and Aragón, C. “Hyperekplexia-associated mutations in the neuronal Glycine Transporter 2”. Neurochemistry International 2019 123:95-100. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuint.2018.05.014.
- Benito-Muñoz, C., Perona, A., Abia, D., dos Santos, H.G., Núñez, E., Aragón, C. and López-Corcuera, B. “Modification of a putative sodium binding site in the glycine transporter 2 influences the chloride dependence of transport”. Front. Mol. Neurosci, 2018, 11(374), 1–18. DOI:10.3389/fnmol.2018.00347.
- Villarejo-López, L, Jiménez, E., Bartolomé-Martín, D., Zafra, F., Lapunzina, P., Aragón, C. and López-Corcuera, B. P2X receptors up-regulate the cell-surface expression of the neuronal glycine transporter GlyT2. 2017 Neuropharmacology 125: 99-116. Epub 17 julio 2017. DOI:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.07.018.
- Arribas-González, E., de Juan Sanz, J., Aragón, C. and López-Corcuera, B. Molecular basis of the dominant-negative effect of a GlyT2 mutation associated with hyperekplexia. J Biol Chem. 2015, 290(4):2150-65. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M114.587055.
- de Juan‐Sanz, J., Núñez, E., Berrocal, M., Corbacho, I., Ibáñez, I., Arribas-González, E. Marcos, D., López‐Corcuera, B., Mata, A.M. and Aragón, C. Presynaptic control of glycine transporter 2 by functional association with Ca2+-ATPase and Na+-Ca2+ exchanger. J Biol Chem. 2014, 289(49):34308-24. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M114.586966.
- de Juan Sanz, J., Núñez, E., Villarejo-López, L., Pérez-Hernández, D., Rodríguez-Fraticelli, A., López-Corcuera, B., Vázquez, J., and Aragón, C. Na+/K+-ATPase is a new interacting partner for the neuronal glycine transporter GlyT2 that down-regulates its expresión in vitro and in vivo. J Neurosci. 2013, 33(35):14269-81. DOI:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1532-13.2013.
- Arribas-González, E., Alonso-Torres, P., Aragón, C. and López-Corcuera, B. Calnexin-assisted biogenesis of the neuronal glycine transporter 2 (GlyT2). PLoS ONE. 2013, 8(5):e63230. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0063230.
- de Juan-Sanz, J, Núñez, E, López-Corcuera, B, and Aragón, C. Constitutive Endocytosis and Turnover of the Neuronal Glycine Transporter GlyT2 Is Dependent on Ubiquitination of a C-Terminal Lysine Cluster. PLoS ONE 2013, 8(3): e58863. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058863.
- Giménez, C., Pérez-Siles, G., Martínez-Villarreal, J., Arribas-González, E., Jiménez, E., Núñez, E., de Juan-Sanz, J., Fernández-Sánchez, E., García-Tardón, N., Ibáñez, I., Romanelli, V., Nevado, J., James, V.M., Topf., M., Thomas, R.H., Desviat, L.R., Aragón, C., Zafra, F., Rees, M.I., Lapunzina, P., Harvey, R.J., and López-Corcuera, B. A novel dominant hyperekplexia mutation Y705C alters trafficking and biochemical properties of the presynaptic glycine transporter GlyT2. J Biol Chem. 2012, 287(34):28986-9002. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.319244.
Doctoral theses:
- Andrés de la Rocha Muñoz (October 5th, 2020. "Estudio del tráfico intracelular, regulación e interactoma de mutantes de GlyT2 asociados a hiperplexia humana”. Universidad Autónoma de Madrid. Director/Supervisor: B. López Corcuera-Carmen Aragón.
- Lucía Villarejo López (May 10th, 2017). "Regulación del transportador neuronal de glicina GlyT2 por el receptor P2X3. Papel en dolor" Universidad Autónoma de Madrid. Director/Supervisor: B. López Corcuera.
- Esther Arribas González (July 4th, 2017). "Biogénesis y regulación del transportador neuronal de glicina GlyT2 y mutantes responsables de hiperplexia humana". Universidad Autónoma de Madrid. Director/Supervisor: B. López Corcuera.
- Pablo Alonso Torres (September 4th, 2017). “Transportador de glicina GlyT2: localización subcelular, asociación con balsas lipídicas y biogénesis”. Universidad Autónoma de Madrid. Director/Supervisor: B. López Corcuera.
- Cristina Benito Muñoz (November 30th, 2018). “Estructura-función del transportador neuronal de glicina GlyT2: localización del sitio Na3 y determinantes de inhibición”. Universidad Autónoma de Madrid. Director/Supervisor: B. López Corcuera.
Book chapters:
- López-Corcuera, B., Benito-Muñoz, C. and Aragón, C. “Glycine transporters in glia cells: structural studies”. Glial Amino Acid Transportes. Advances in Neurobiology. Arturo Ortega and Arne Schousboe Eds. Springer. Adv Neurobiol. 2017, 16:13-32. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-55769-4_2.
Other activities:
- The group belongs to the Institute of Investigación Biosanitaria IdiPAZ from November 2010 as research group “Implication of glycinergic and glutamatergic systems in pathologies of the Central Nervous System”.




















