Regulation of mRNA translation in eukaryotes and its implications for organismal life
Research summary:
We investigate how eukaryotic systems regulate translation initiation at both global and message-specific manner, trying to identify new elements in ribosomes and mRNAs, and new initiation factor (eIFs) activities involved in the differential translation of mRNAs during cell proliferation and stress response. We have identified the ES6S region of 40S ribosomal subunit as the gateway for mRNA entry and secondary structure unwinding during the scanning process, so that blocking ES6S region differentially affected the expression of some proto-oncogenes (H-Ras, CCND3, ODC-1, etc.) and other genes involved in signal transduction with long and structured 5´UTR mRNAs. We are currently evaluating the anti-tumoral activity of oligonucleotides and aptamer molecules targeting the ES6S of 40S subunit.
We aim to understand how cells reprogramme translation during the stress response in yeast and mammals by modulating the activity of eIF2 and eIF2A factors, and the physiological impact of this response on cell and organismal adaptation, survival and ageing. Thus, preventing eIF2α phosphorylation not only impaired stress response, but also accelerated ageing in yeast by a mechanism that involves proteostasis disruption.
We are also studying how alphaviruses have evolved to adapt translation of their mRNA to stress conditions in infected cells and tissues, a useful model that is bringing new insights into the antiviral responses in mammals, allowing us to develop modified viruses with increased oncoselectivity for virotherapy of tumors.
We use several model organisms from yeast to human, combining molecular genetics, structural analysis, high-throughput techniques and animal models, together with bioinformatics and systems biology approaches.

Figure 1. Word cloud of research topics studied in our lab.
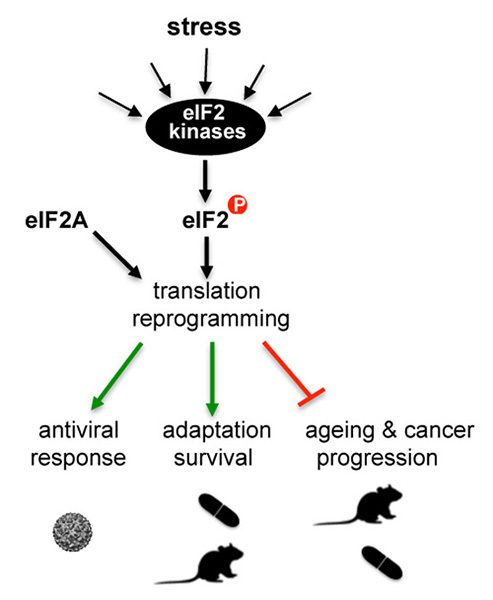
Figure 2. Stress-induced eIF2α phosphorylation promotes a general attenuation of protein synthesis, and the simultaneous translational activation of a number of mRNAs (about 300 in humans) involved in stress response and survival. Both events are necessary for the adaptive response of cells and tissues to stress, which also shapes some long-term physiological aspects of organismal life such as survival and ageing. Non-canonical translation of specific mRNAs requires both eIF2 inactivation and the participation of some alternative initiation factors such as eIF2A.
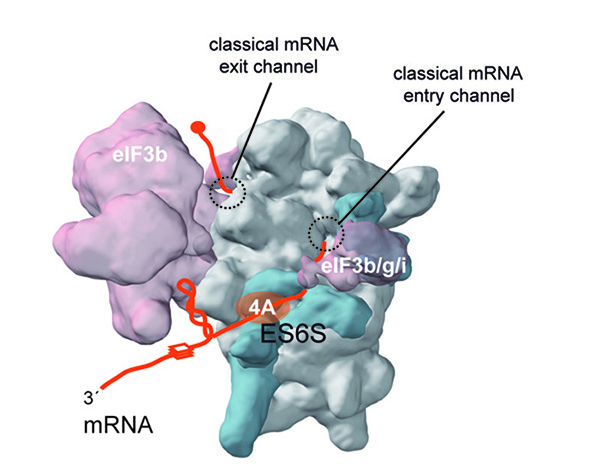
Figure 3. Model of the scanning 48S pre-initiation complex (PIC) showing the path of mRNA through the ES6S region of the 40S ribosomal subunit. According to our data, the mRNA is threaded in the ES6S region and unwound by associated RNA helicases (eIF4A) before reaching the classical mRNA entry channel. Stem-loop (helix) and G-quadruplex (box) are structural elements present in the 5´UTR of the mRNA. For simplicity, only the helicase component (eIF4A) of the eIF4F complex is shown.

| Last name | Name | Laboratory | Ext.* | Professional category | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alcalde García | José | 106 | 4534 | jalcalde(at)cbm.csic.es | E.Ayudantes De Invest. De Los Oo.Publicos De Investigacion |
| Berlanga Chiquero | Juan José | 106 | 4714/4534 | jberlanga(at)cbm.csic.es | Profesor Titular Universidad, GA |
| Jiménez Saucedo | Tamara | 106 | 4534 | tjimenez(at)cbm.csic.com | Titulado Sup.de Actividades Técn. y Profes. GP1 |
| Rodríguez Gabriel | Miguel Ángel | 106 | 4816 | marodriguez(at)cbm.csic.es | Profesor Titular Universidad, GA |
| Ventoso Bande | Iván | 126/114.4( despacho) | 4809 | iventoso(at)cbm.csic.es | Profesor Titular Universidad, GA |
Relevant publications:
- Díaz-López I, Toribio R, Berlanga JJ, Ventoso I (2019) An mRNA-binding channel in the ES6S region of the translation 48S-PIC promotes RNA unwinding and scanning. Elife. 8. doi: 10.7554/eLife.48246.
- Toribio R, Díaz-López I, Boskovic J, Ventoso I (2018) Translation initiation of alphavirus mRNA reveals new insights into the topology of the 48S initiation complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 46(8): 4176-4187. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky071.
- Martín R, Berlanga JJ, de Haro C (2013) New roles of the fission yeast eIF2α kinases Hri1 and Gcn2 in response to nutritional stress. J Cell Sci. 126: 3010-3020.
- Matia-Gonzalez AM, Hasan A, Moe, GH, Mata J, Rodriguez-Gabriel MA (2013) Functional characterization of Upf1 targets in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. RNA Biol. 10: 1057-1065.
- Toribio R, Ventoso I (2010) Inhibition of host translation by virus infection in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 107(21): 9837-42. doi:10.1073/pnas.1 004110107.
- Ventoso I, Sanz MA, Molina S, Berlanga JJ, Carrasco L, Esteban M (2006) Translational resistance of late alphavirus mRNA to eIF2alpha phosphorylation: a strategy to overcome the antiviral effect of protein kinase PKR. Genes Dev. 20(1):87-100.
- Berlanga JJ, Ventoso I, Harding HP, Deng J, Ron D, Sonenberg N, Carrasco L, de Haro C (2006) Antiviral effect of the mammalian translation initiation factor 2alpha kinase GCN2 against RNA viruses. EMBO J. 25(8):1730-40.
Doctoral theses:
- Tamara Jiménez Saucedo. Role of eIF2α-dependent translational regulation in aging. Dpto. Biología Molecular. UAM 2020. Sobresaliente Cum Laude.
- Irene Díaz López. Involvement of ES6S region of 40S subunit in mRNA threading and scanning during translation initiation. Dpto. Biología Molecular. UAM 2019. Sobresaliente Cum Laude.
- Marina Portantier. Papel del complejo Ccr4-Not en la respuesta a estrés mediada por la MAPK Spc1 en Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Dpto. Biología Molecular. UAM 2013. Sobresaliente Cum Laude.
- Javier del Pino García. Interacción funcional de la eIF2a quinasa GCN2 con el virus de la inmunodeficiencia humana VIH-1. Dpto. Biología Molecular. UAM 2012. Sobresaliente Cum Laude.
- Ruth Martín Martín. Caracterización funcional de las eIF2α quinasas de Schizosaccharomyces pombe en distintas situaciones de estrés. Dpto. Biología Molecular. UAM 2012. Sobresaliente Cum Laude.
- Ana María Matía González. Role of Upf1 and Csx1 on posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Dpto. Biología Molecular. UAM 2011. Sobresaliente Cum Laude.
- René Toribio López. Cambios Traduccionales que regulan la interacción virus hospedador. Implicación en el desarrollo de virus oncolíticos. Dpto. Biología Molecular. UAM 2010. Sobresaliente Cum Laude.
- Jael Sotelo Álvarez. Wip1: una nueva proteína moduladora de la diferenciación sexual en Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Dpto. Microbiología II. UCM 2010. Sobresaliente Cum Laude.
- Isabela Alonso González. Caracterización funcional de la elF2α quinasa GCN2 de células de mamífero. Dpto. Biología Molecular. UAM 2009. Sobresaliente Cum Laude.




















