Cell communication in homeostasis and disease through new Gq-GPCR signaling nodes
Research summary:
Cell-cell communication and the interactions that occur between them are a key aspect in the maintenance of cellular homeostasis, regulating individual cellular processes and intercellular relationships. When cells do not interact properly or incorrectly decode molecular messages, a pathological process is triggered.
The main objective of our group is to understand the functional impact, at the cellular and organismal level, of new interactions of important G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling nodes, relevant in the maintenance of cellular homeostasis (eg. Gαq and GRK2), and how changes in them can affect the progression of pathologies, using cell and animal models with altered expression/activity of these proteins, as well as patient samples or animal models of disease. We will focus particularly on the functional impact of these new interactions and their modulation by accessory proteins (such as GRKs, AGS, RGS, caveolin, Ric8), on cell death processes, integration of nutrient sensing/autophagy signals, and endothelial dysfunction in the development of inflammatory/metabolic pathologies and cancer.
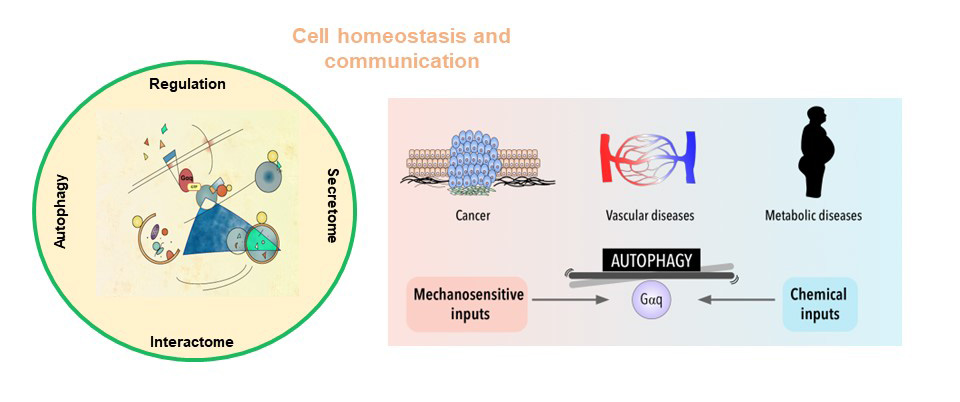
Fig 1. The Gαq interactome and its functional repercussions
The Gαq interactome has expanded considerably with the description of new effectors and our group has contributed to this, through the identification of a new interaction region in Gαq, different from the classic effector binding region. This non-canonical Gαq signaling has turned out to be relevant in the development of cardiovascular pathologies and, furthermore, recent results have revealed the novel role of Gαq as a central modulator of mTORC1, contributing to the regulation of the autophagic process and thus to the maintenance of cell homeostasis, depending on nutrients fluctuations. These new Gαq interaction networks appear to be important in the regulation of endothelial function. Furthermore, Gαq is known to interact with various cytoskeletal components as well as important membrane microdomain organizers, suggesting the existence of signaling complexes that might be limited to specific subcellular environments.
In turn, we have also revealed a relevant role of one of the main regulators of these Gq-GPCR signaling pathways, GRK2, in the maintenance of the epithelial phenotype of stratified epithelia and demonstrated how its absence contributes to the development and malignancy of oral carcinomas (HNSCC), also revealing an important role of this kinase in epidermal homeostasis and in its inflammatory response.
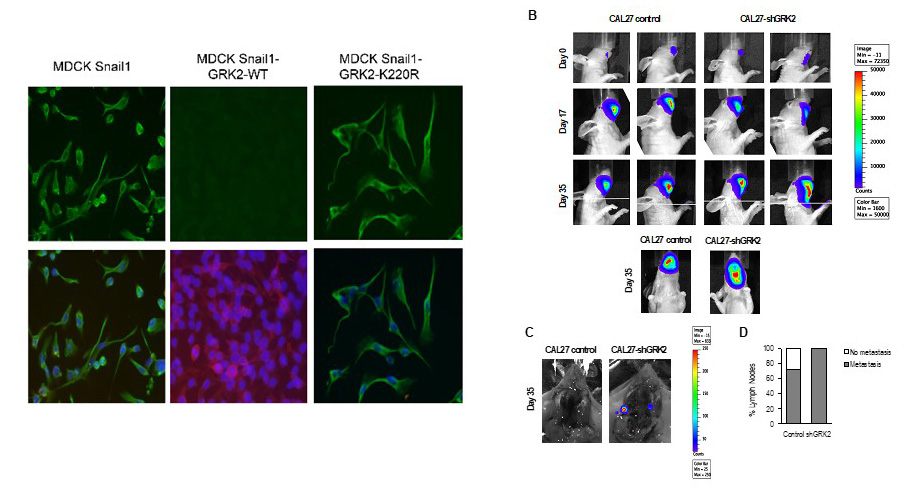
Figure 2. The absence of GRK2 contributes to the activation of EMT programs and tumor malignancy in stratified epithelia.
To deepen a better understanding of the contribution of these signaling nodes to cellular communication between different cell types, both under physiological and pathological conditions, regulating exosome trafficking/autophagy, endothelial dysfunction/angiogenesis and extracellular matrix remodeling (including: normal or activated fibroblasts (CAF), endothelial cells, immune system cells and/or tumor cells), taking into account their respective secretomes, will contribute to the development of more effective therapies in inflammatory/metabolic and tumor contexts.
Some of these research objectives imply active collaborations with other members of our Unit at the CBMSO, as well as through CIBER Cardiovascular (CIBER-CV, ISCIII), Network of Biomedicine Integramune, (Comunidad de Madrid), as well as our affiliation to the Institute of Sanitary Research La Princesa.

| Apellidos | Nombre | Laboratorio | Ext.* | Categoría profesional | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ribas Núñez | Catalina | 304 | 4728 | cribas(at)cbm.csic.es |
Profesora Titular Universidad |
| Navarro Lérida | Inmaculada | 304 | 4656 | ilerida(at)cbm.csic.es | Profesora Ayudante Doctor |
| García Mateos | Dafne | 304/320 | 4656/4652 | dafne.garcia(at)cbm.csic.es | Técnico superior UAM |
| Asensio López | Alejandro | 304 | 4656 | alejandro.asensio(at)cbm.csic.es | Contrato Predoctoral FPI |
| Jiménez López | Isabel | 304 | 4656 | mariaisabeljimenez1999(at)gmail.com | Contrato Investigo CAM |
| Romo Gallo | Ana | 304 | 4656 | ana.romog(at)estudiante.uam.es | Estudiante de Grado |
| Delgado Arévalo | Cristina | 304/320 | 4656/4652 | cdelgado(at)cbm.csic.es | Técnico Superior UAM |
| Vázquez de Oro | Estefanía | 304/320 | 4656/4652 | evazquez(at)cbm.csic.es | Tco. de Investigación y Laboratorio |
Relevant publications:
- Gq Signaling in Autophagy Control: Between Chemical and Mechanical Cues. Navarro-Lérida I, Aragay AM, Asensio A, Ribas C. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Aug 18;11(8):1599. doi: 10.3390/antiox11081599.
- Gαq activation modulates autophagy by promoting mTORC1 signaling. Cabezudo S, Sanz-Flores M, Caballero A, Tasset I, Rebollo E, Diaz A, Aragay AM, Cuervo AM, Mayor F Jr, Ribas C. Nature Comm. 2021 Jul 27;12(1):4540. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24811-4.
- G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 safeguards epithelial phenotype in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Palacios-García J, Sanz-Flores M, Asensio A, Alvarado R, Rojo-Berciano S, Stamatakis K, Paramio JM, Cano A, Nieto MÁ, García-Escudero R, Mayor F Jr, Ribas C. Int J Cancer. 2019 Dec 18. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32838.
- G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2) as a multifunctional signaling hub. Penela P, Ribas C, Sánchez-Madrid F, Mayor F Jr. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Nov;76(22):4423-4446. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03274-3.
- Gαq signalling: the new and the old. Sánchez-Fernández G, Cabezudo S, García-Hoz C, Benincá C, Aragay AM, Mayor F Jr, Ribas C. Cell Signal. 2014 May;26(5):833-48. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.01.010.
- G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRKs) in tumorigenesis and cancer progression: GPCR regulators and signaling hubs. Nogués L, Palacios-García J, Reglero C, Rivas V, Neves M, Ribas C, Penela P, Mayor F Jr. Semin Cancer Biol. 2018 Feb;48:78-90. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.04.013.
- Protein Kinase C ζ Interacts with a Novel Binding Region of Gαq to Act as a Functional Effector. Sánchez-Fernández G, Cabezudo S, Caballero Á, García-Hoz C, Tall GG, Klett J, Michnick SW, Mayor F Jr, Ribas C. J Biol Chem. 2016 Apr 29;291(18):9513-25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.684308.
- ERK5 activation by Gq-coupled muscarinic receptors is independent of receptor internalization and β-arrestin recruitment. Sánchez-Fernández G, Cabezudo S, García-Hoz C, Tobin AB, Mayor F Jr, Ribas C. PLoS One. 2013 Dec 17;8(12):e84174. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084174.
- Protein kinase C (PKC)ζ-mediated Gαq stimulation of ERK5 protein pathway in cardiomyocytes and cardiac fibroblasts. García-Hoz C, Sánchez-Fernández G, García-Escudero R, Fernández-Velasco M, Palacios-García J, Ruiz-Meana M, Díaz-Meco MT, Leitges M, Moscat J, García-Dorado D, Boscá L, Mayor F Jr, Ribas C. J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 2;287(10):7792-802. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.282210.
- G alpha(q) acts as an adaptor protein in protein kinase C zeta (PKCzeta)-mediated ERK5 activation by G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR). García-Hoz C, Sánchez-Fernández G, Díaz-Meco MT, Moscat J, Mayor F, Ribas C. J Biol Chem. 2010 Apr 30;285(18):13480-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.098699.




















