Scientific Program
Tissue and organ homeostasis
RESEARCH GROUP
Extracellular matrix remodeling in the cardiovascular system

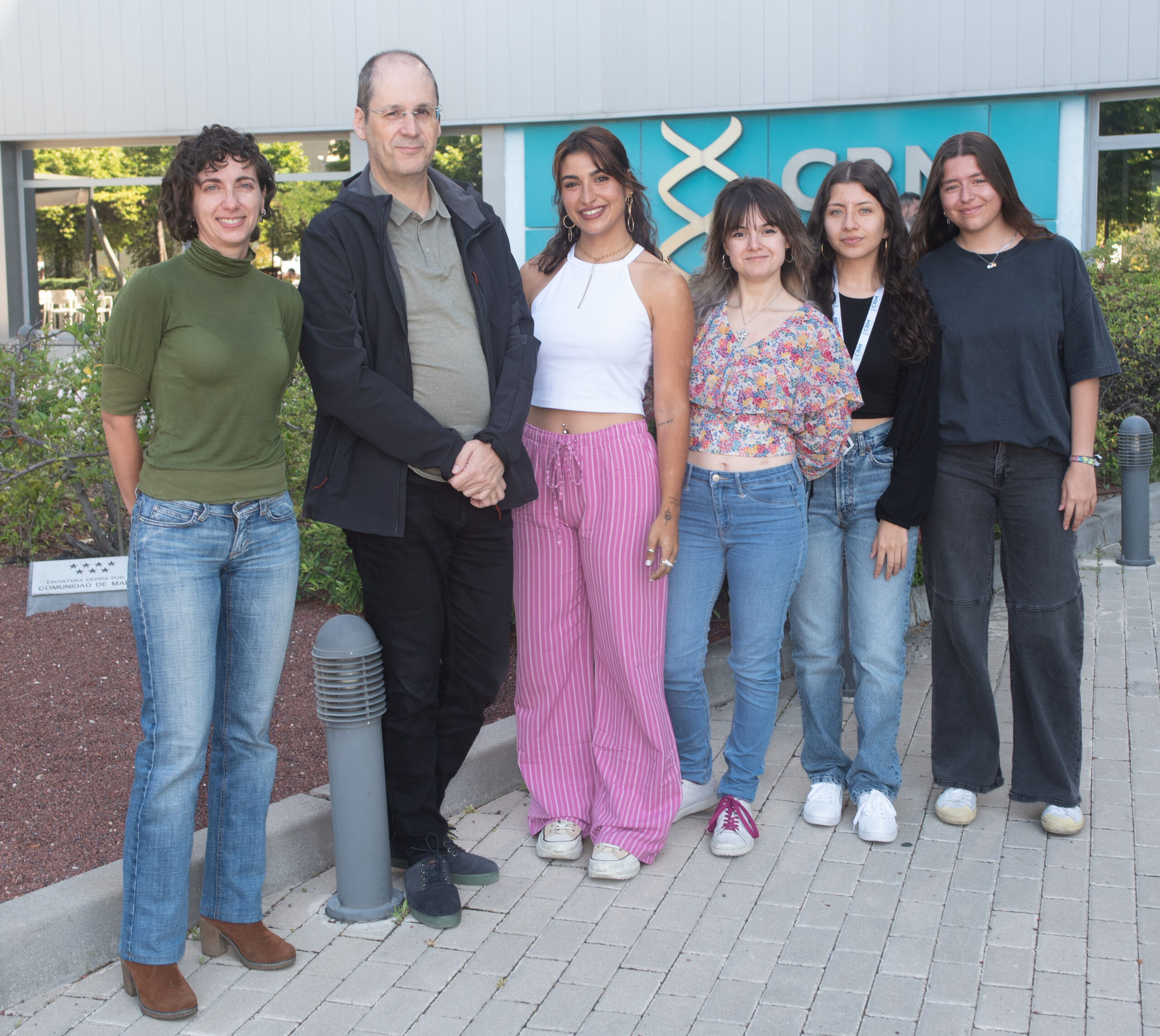
Fernando Rodríguez Pascual
The goal of our lab is to understand the mechanisms by which cells produce and deposit extracellular matrix components, mainly focused on the regulation of collagen modifying enzymes. Within this context, our group has established a number of cellular and animal models and explore how these mechanisms influence the development of fibrosis and cardiovascular diseases.
Research
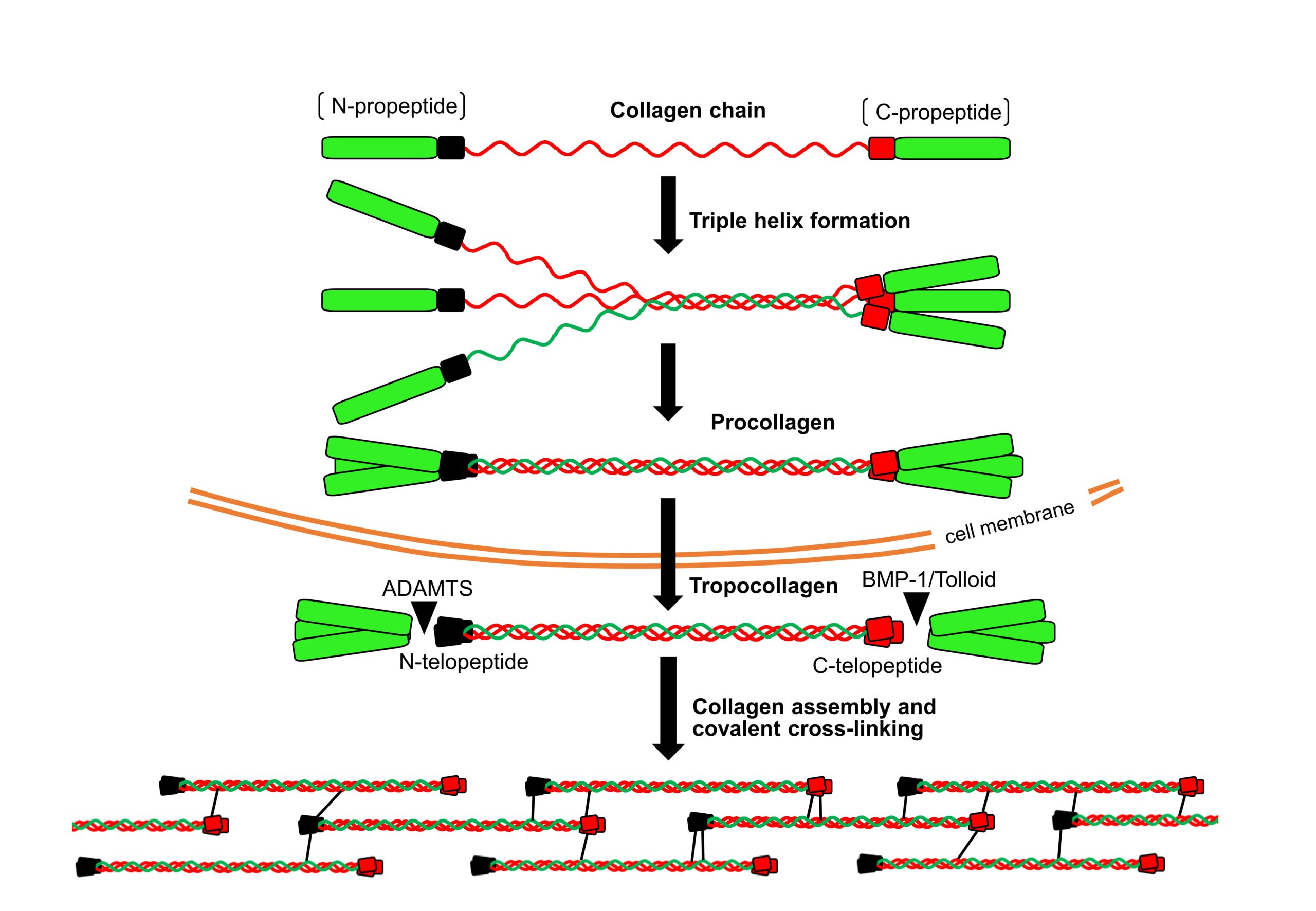
Proper synthesis and assembly of extracellular matrix components is essential to provide cells and tissues with their biological and biomechanical properties. Biosynthesis of collagen, the most important component of the extracellular matrix, requires the commitment of a set of enzymatic components, including prolyl and lysyl hydroxylases and lysyl oxidases, responsible for a number of post-translational modifications, many of them unique for collagen. The action of these collagen remodeling enzymes is essential to provide the collagen molecule with its capacity to deposit on the extracellular matrix and form supramolecular structures like bones, teeth or blood vessels, and, therefore, they exert an important influence in homeostasis and disease. By the establishment of different cellular and animal models, in our group, we investigate the molecular mechanisms regulating the biological activity of collagen remodeling enzymes, as well as their pathophysiological relevance in the development of fibrosis and cardiovascular diseases.
Group members

Fernando Rodríguez Pascual
Lab.: 103 Ext.: 4505
frodriguez(at)cbm.csic.es

Raquel Jiménez Sánchez
Lab.: 103 Ext.: 4456
rjimenez(at)cbm.csic.es

Verónica Romero Albillo
Lab.: 103 Ext.: 4505
vromero(at)cbm.csic.es

Marta Navarro Gutiérrez
Lab.: 103 Ext.: 4505
marta.navarro(at)cbm.csic.es

Christopher Enriquez Pinargote
Lab.: 103 Ext.: 4505
Selected publications

Multimerization of HIF enhances transcription of target genes containing the hypoxia ancillary sequence
Tamara Rosell-Garcia et al.

A hierarchical network of hypoxia-inducible factor and SMAD proteins governs procollagen lysyl hydroxylase 2 induction by hypoxia and transforming growth factor β1
Tamara Rosell-García et al.

Differential cleavage of lysyl oxidase by the metalloproteinases BMP1 and ADAMTS2/14 regulates collagen binding through a tyrosine sulfate domain LOX cleavage regulates collagen binding
Tamara Rosell-García et al.
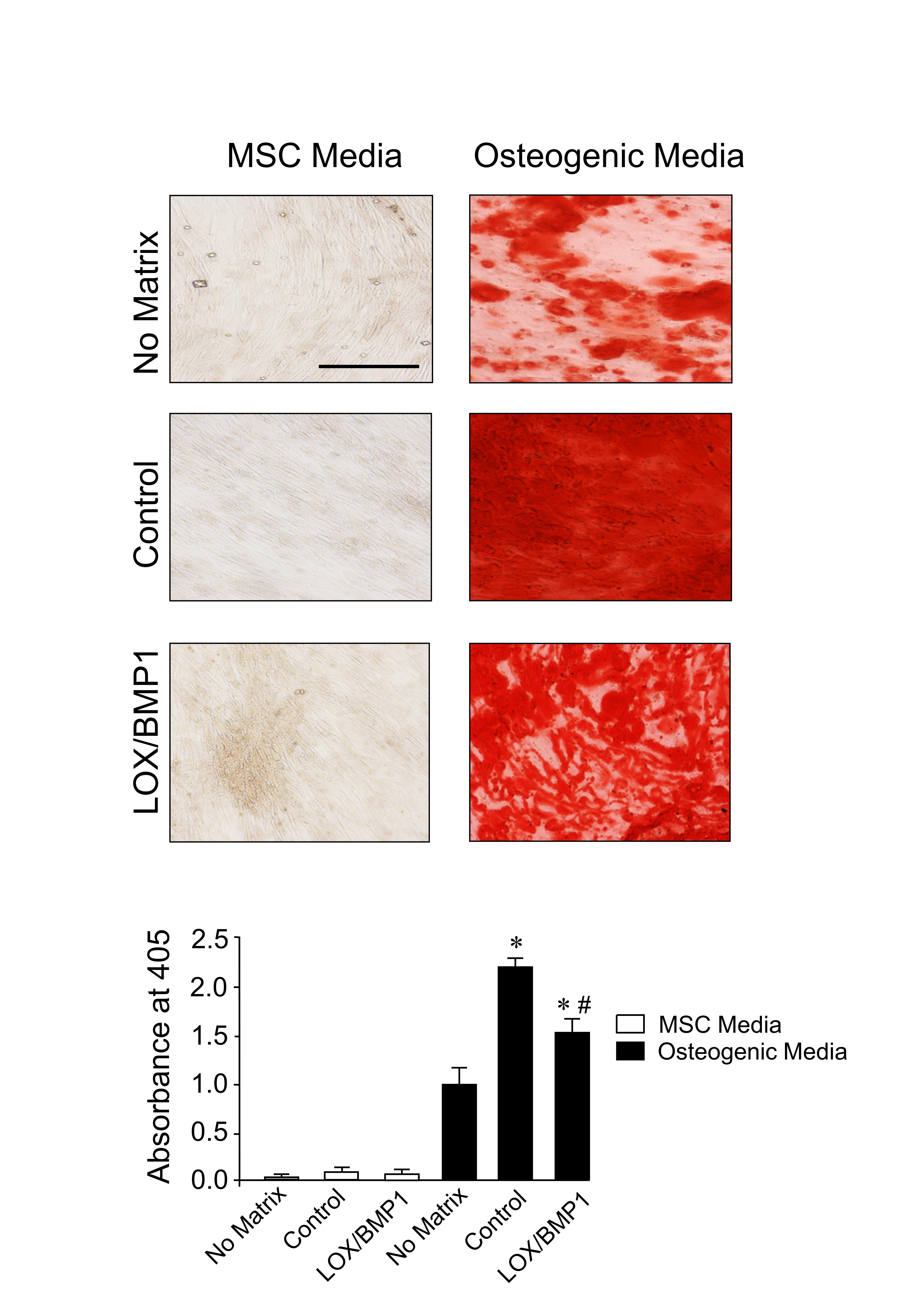
Enhancement of collagen deposition and cross-linking by coupling lysyl oxidase with bone morphogenetic protein-1 and its application in tissue engineering
T. Rosell-Garcia et al.