Internal initiation of translation in eukaryotic mRNAs
Research summary:
Our aims are focused to understand the principles guiding alternative mechanisms of translation initiation in eukaryotes through the characterization of RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) interacting with mRNAs. Internal ribosome entry sites (IRES) are non-coding RNA regions that substitute the function of the 5’ terminal cap of mRNAs, the anchoring point of the translation machinery. Our specific aims were the identification of proteins modulating IRES activity, the evaluation of synergism and/or interference with other factors, and the understanding of structural constraints which are essential for its activity. Among other RBPs, we have shown that Gemin5 interacts with viral IRES as well as a selective group of cellular mRNAs. Gemin5 is a multitasking protein that forms part of the survival of motor neuron (SMN) complex, but also performs a translation regulatory role. The N-terminal domain of Gemin5 is involved in the interaction with the ribosome and the snRNAs, whereas the C-terminal region harbors a non-conventional RNA-binding site (RBS1). Identification of the RNA partners of the RBS1 domain unveiled a feedback loop with its own mRNA, counteracting the negative effect of Gemin5 on translation. The RBS1 moiety harbors an intrinsically disordered region (IDR) which coevolved with the RNA-interacting region, revealing the evolutionary selection of the RNA-protein interaction module. The midle region of the protein harbors a dimerization domain consisting of a tetratricopeptide (TPR)-like domain that self-assembles into a canoe-shaped dimer (Figure 1). The dimerization module is functional in living cells driving the interaction between the half C-terminal fragment and the full-length Gemin5, which anchors splicing and translation factors. Disruption of the dimerization capacity of Gemin5 prevents this interaction and abrogates translation enhancement induced by the C-terminal fragment of the protein. Notably, Gemin5 variants recently found in patients with neurological disorders harbor structural defects that impair dimerization, reduce translation, and show strong protein interactome decrease (Figure 2). In summary, this protein provides an important platform for RNP interactions, controlling translation of selective mRNAs, including ribosomal protein and histones, critical for cell growth, beyond being a key actor in spliceosome assembly.
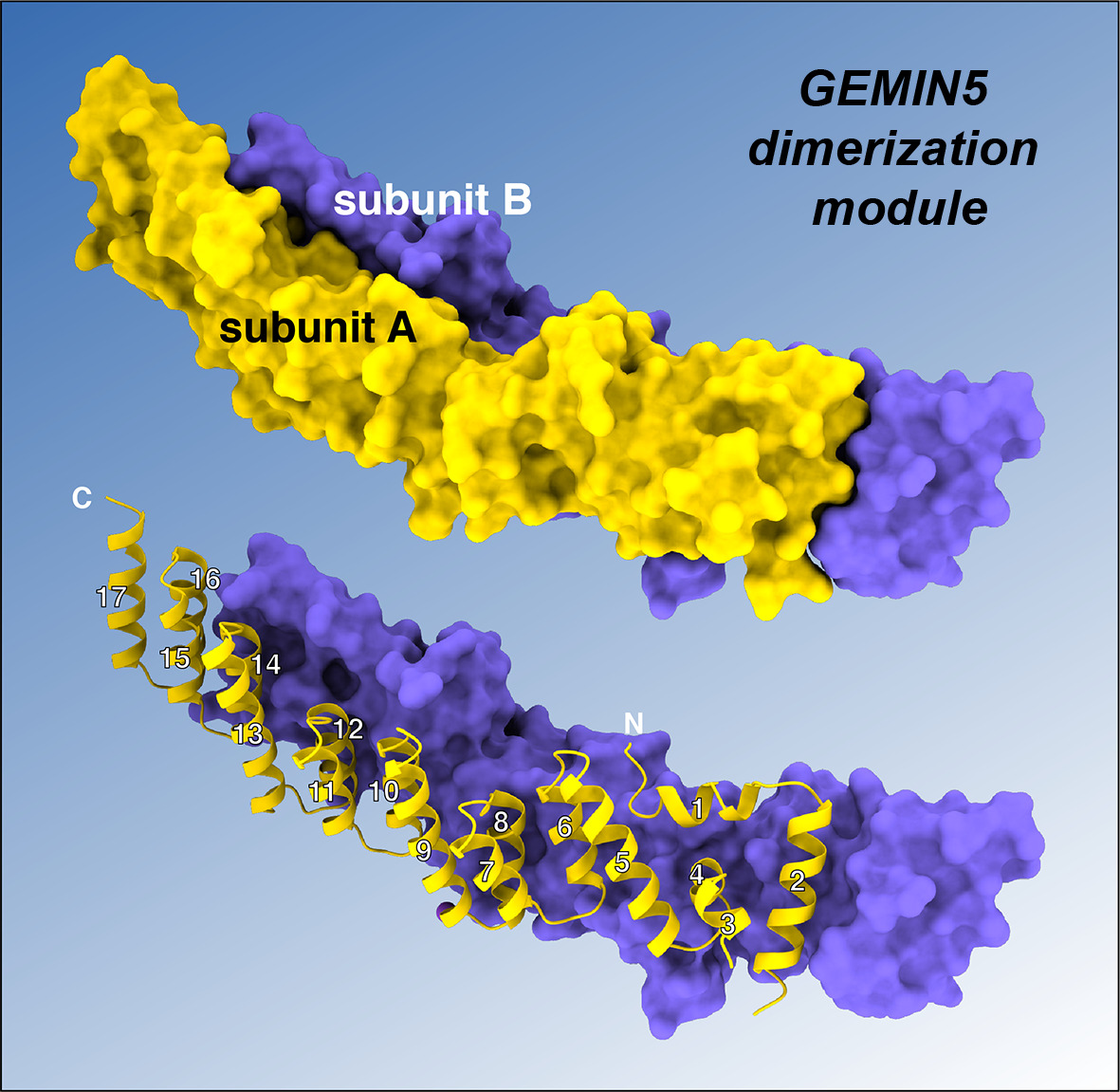
Figure 1. Gemin5 dimerization domain. The homodimer structure consists of a tetratricopeptide (TPR)-like structure. Each subunit is shown in different color. The numbers for the 17 helices are indicated.
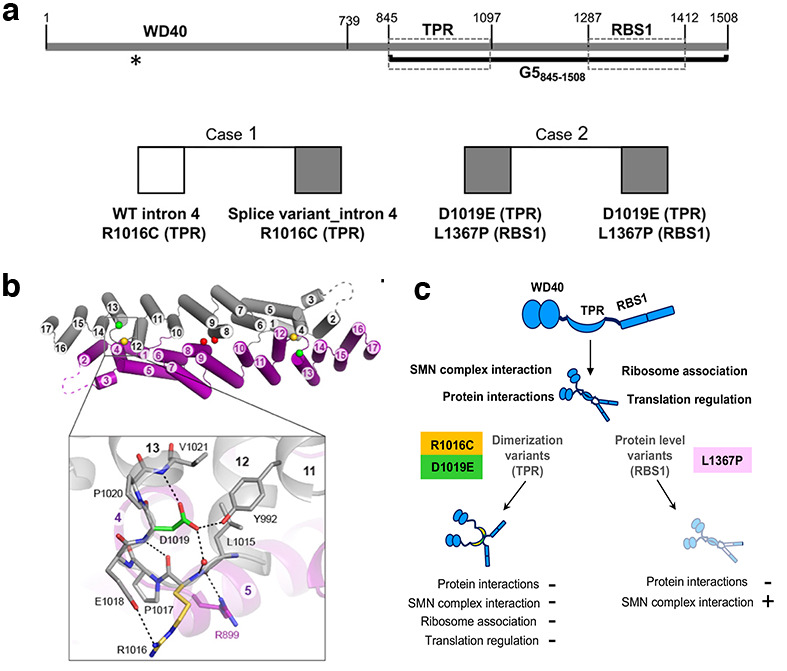
Figure 2. Gemin5 protein organization, pathogenic variants, and structural properties of the variants. a Structural domains of the protein and summary of Gemin5 biallelic variants found in patients developing neurodevelopmental disorders. b Gemin5 TPR-like homodimer depicting the position of mutated residues. Zoom view of the loop a12-13 with residue R1016 (yellow) and D1019 (green). c Functions affected by pathogenic variants on the dimerization module and the RBS1 domain of Gemin5

| Last name | Name | Laboratory | Ext.* | Professional category | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abellán Pérez | Salvador | 309 | 4649 | sabellan(at)cbm.csic.es | M3 Predoc.formación |
| Francisco Velilla | Mª del Rosario | 309 | 4649 | rfrancisco(at)cbm.csic.es | M3 |
| Martínez Salas | Encarnación | 309 | 4619 | emartinez(at)cbm.csic.es | E. Profesores de Investigación de Organismos Públicos de Investigación |
| Ramajo Alonso | Jorge | 309 | 4649 | j.ramajo(at)csic.es | Técnico Sup. Actividades Téc. y Profes. GP3 |
Relevant publications:
- Qiong Guo Q, Zhao S, Francisco-Velilla R, Zhang J, Embarc-Buh A, Abellan S, Lv M, Tang P, Gong Q, Shen H, Sun L, Yao X, Min J, Shi Y, Martínez-Salas E, Zhang K, Xu C. Structural basis for Gemin5 decamer-mediated mRNA binding. Nat Comm 2022;13(1):5166. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32883-z.
- Embarc-Buh A, Francisco-Velilla R, Garcia-Martin JA, Abellan S, Ramajo R, Martinez-Salas E. Gemin5-dependent RNA association with polysomes enables selective translation of ribosomal and histone mRNAs. CMLS 2022;79(9):490. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04519-4.
- Rajan DS, Kour S, Fortuna TR, Cousin MA, Barnett SS, Niu Z, Babovic-Vuksanovic D, Klee EW, Kirmse B, Innes M, Rydning SL, Selmer KK, Vigeland MD, Erichsen AK, Nemeth AH, Millan F, DeVile C, Fawcett K, Legendre A, Sims D, Schnekenberg RP, Burglen L, Mercier S, Bakhtiari S, Martinez-Salas E, Wigby K, Lenberg J, Friedman JR, Kruer MC, Pandey UB. Autosomal Recessive Cerebellar Atrophy and Spastic Ataxia in Patients With Pathogenic Biallelic Variants in GEMIN5. Front Cell Dev Biol 2022;10:783762. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.783762.
- Francisco-Velilla R, Embarc-Buh A, Del Caño-Ochoa F, Abellan S, Vilar M, Alvarez S, Fernandez-Jaen A, Kour S, Rajan DS, Pandey UB, Ramón-Maiques S, Martinez-Salas E. Functional and structural deficiencies of Gemin5 variants associated with neurological disorders. Life Sci Alliance 2022;5(7):e202201403. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202201403.
- Francisco-Velilla R, Embarc-Buh A, Abellan S, Martinez-Salas E. Picornavirus translation strategies. FEBS Open Bio. 2022;12(6):1125-1141. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13400.
- Escos A, Martín-Gómez J, González-Romero D, Díaz-Mora E, Francisco-Velilla R, Santiago C, Cuezva JM, Domínguez-Zorita S, Martínez-Salas E, Sonenberg N, Sanz-Ezquerro JJ, Mehdi Jafarnejad S, Cuenda A. TPL2 kinase expression is regulated by p38γ/p38δ-dependent association of Aconitase-1 with TPL2 mRNA. PNAS 2022;119(35):e2204752119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2204752119.
- Embarc-Buh A, Francisco-Velilla R, Camero S, Perez-Cañadillas JM, Martínez-Salas E. The RBS1 domain of Gemin5 is intrinsically unstructured and interacts with RNA trough conserved Arg and aromatic residues RNA Biology 2021;18(sup1):496-506. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2021.1962666.
- Fernandez-Chamorro J, Francisco-Velilla R, Embarck-Buk A, Martínez-Salas E. Identification of novel RNA-binding proteins recognizing RNA structural elements. Meth Mol Biol 2021;2323:109-119. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1499-0_9.
- Embarc-Buh A, Francisco-Velilla R, Martínez-Salas E. RNA-binding proteins at the host-pathogen interface targeting viral regulatory elements. Viruses 2021;13(6):952 doi: 10.3390/v13060952.
- Francisco-Velilla R, Embarc-Buh A, Rangel-Guerrero S, Basu S, Kundu S, Martínez-Salas E. RNA-protein coevolution study of Gemin5 uncovers the role of the PXSS motif of RBS1 domain for RNA binding. RNA Biology 2020;17(9), 1331-1341. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1762054.
- Martínez-Salas E, Embarc-Buh A, Francisco-Velilla R. Emerging roles of Gemin5: from snRNPs to translation control. IJMS 2020;21(11):3868. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113868.
- Saiz M, Martinez-Salas E. Uncovering targets of the Leader protease: Linking RNA-mediated pathways and antiviral defense. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 2021;12(4):e1645. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1645.
- Rodríguez Pulido M, Martínez-Salas E, Sobrino F, Sáiz M. MDA5 cleavage by the Leader protease of foot-and-mouth disease virus reveals its pleiotropic effect against the host antiviral response. Cell Death Dis 2020;11(8):718. doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-02931-x
- Moreno-Morcillo, M, Francisco-Velilla, R., Embarc-Buh, A., Fernandez-Chamorro, J, Ramon-Maiques, S., and Martínez-Salas, E. (2020) Structural basis for the dimerization of Gemin5 and its role in protein recruitment and translation control. Nucleic Acids Res, 48(2):788-801.
- Francisco-Velilla R, Embarc-Buh A, Martinez-Salas E (2019) RNA-binding modes impacting on translation control: the versatile multidomain protein Gemin5. BioEssays 41(4):e1800241.
- Fernandez-Chamorro J, Francisco-Velilla R, Ramajo J, Martinez-Salas E (2019) IRES-driven RNA localization at ER-Golgi compartment is mediated by RAB1b and ARF5. Life Sci Alliance 2(1). pii: e201800131.
- Lozano G, Francisco-Velilla R, Martinez-Salas E (2018) Deconstructing IRES elements: an update of structural motifs and functional divergences. Open Biology 8 (11). pii: 180155.
- Francisco-Velilla R, Fernandez-Chamorro J, Dotu I, Martinez-Salas E (2018) The RNA landscape of the non-canonical RNA-binding domain of Gemin5 unveils a feedback loop with its own mRNA counteracting the negative effect on translation. Nucleic Acids Res 46, 7339-7353.
- Lozano G, Francisco-Velilla R, Martinez-Salas E (2018) Ribosome-dependent conformational flexibility changes and RNA dynamics of IRES domains revealed by differential SHAPE. Sci Rep 8(1): 5545.
- Galan A, Lozano G, Piñeiro D, Martinez-Salas E (2017) G3BP1 interacts directly with the FMDV IRES and negatively regulates translation. FEBS J 284, 3202-3217.
- Diaz-Toledano R, Lozano G, Martínez-Salas E (2017) In-cell SHAPE uncovers dynamic interactions between the untranslated regions of the foot-and-mouth disease virus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res 45, 1416-1432.
- Francisco-Velilla R, Fernandez-Chamorro J, Ramajo J, Martínez-Salas, E. (2016) The RNA-binding protein Gemin5 binds directly to the ribosome and regulates global translation. Nucleic Acids Res 44, 8335-8351.
- Lozano G, Jimenez-Aparicio R, Herrero S, Martínez-Salas E (2016) Fingerprinting the junctions of RNA secondary structure by an open-paddle wheel diruthenium compound. RNA 22, 330-338.




















