Nitric Oxide and bioactive lipids signalling in the immune response
Research summary:
Nitric oxide (NO) and bioactive lipids as nitro-fatty acids (NO2-FA) or prostaglandins, are key mediators for maintaining cellular homeostasis, with an essential role in inflammation. Recent studies indicate that both mediators can play an important role in the modulation of the immune response. Our research lines are dedicated to the study the role played by NO as well as nitro and oxo modified fatty acids in inflammation and in the activation and differentiation of T lymphocytes. In this sense, we are currently studying the actions exerted by NO, nitro fatty acids and prostanoids on the activation of human T lymphocytes, analysing their involvement in the regulation of gene expression and activation of transcription factors triggered from the T cell receptor. We are also interested in the analysis of other parameters of activation such as chemotaxis, intercellular adhesion and the organization of adhesion and signalling receptors at the immune synapse. In addition, we are also examining the potential actions of these compounds on the selection of the adaptive immune response in human T lymphocytes.
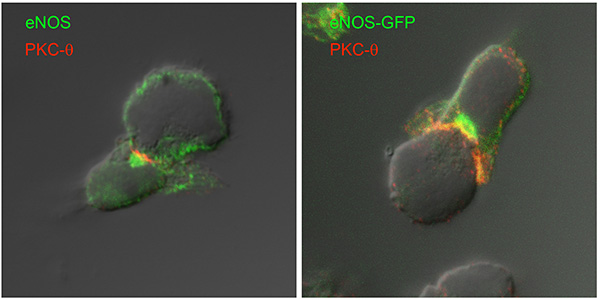
Figure 1. Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase controls the coalescence of Protein Kinase C-θ (PKC-θ) at the central Supramolecular Activation Cluster (c-SMAC) of the T Cell Immune Synapse (IS). The cellular localization of PKC-θ (red) and endogenous eNOS or overexpressed eNOS-green fluorescent protein (eNOS-GFP) at the IS of a superantigen-specific T cell-APC conjugate is shown.
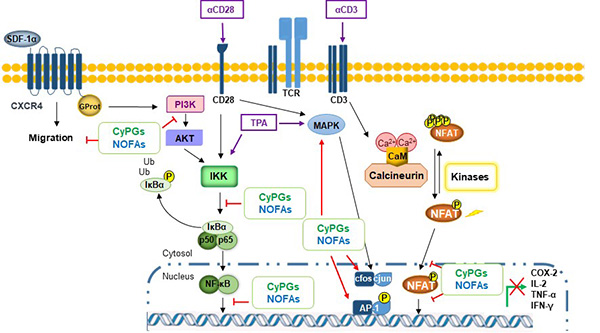
Figure 2. Model of CyPG and NO2FA actions on T cell activation. Upon signaling through the T cell receptor (TCR), different signaling pathways are activated, that ultimately promote the activation of various transcription factors, including NF-κB, AP-1 and NFAT. Activation of these factors is central for the transcription of essential genes in the immune and inflammatory response, such as IL-2, TNF-α and IFN-γ, among others. Electrophilic fatty acids such as Cyclopentenones (CyPGs) and Nitro fatty acids (NO2FA) interfere on different steps in T cell activation process, resulting in changes on gene expression in activated T lymphocytes as well as in T cell migration, which accounts for their anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory properties.

| Last name | Name | Laboratory | Ext.* | Professional category | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bago Plaza | Ángel | 126 | 4542 | angel.bago(at)cbm.csic.es | Titulado Sup. Actividades Tecn. y Prof.GP1 |
| Cayuela Zorita | Laura | 126 | 4549 | Técnico Superior de Actividades Técnicas y Profes.GP3 | |
| Fernández Barroso | Elena | 126 | 4549 | Estudiante TFG | |
| Iñiguez Peña | Miguel Ángel | 126/114.5 | 4508/4549 | mainiguez(at)cbm.csic.es | Profesor Titular Universidad, GA |
| Renshaw Calderón | Ana | 126 | 4549 | arenshaw(at)cbm.csic.es | Ayudante Investigación |
| Serrador Peiró | Juan Manuel | 126/114.6 | 4547 | jmserrador(at)cbm.csic.es | E.Científicos Titulares de Organismos Públicos de Investigación |
Relevant publications:
- Almudena García-Ortiz and Juan M. Serrador. (2018) Nitric oxide signalling in T cell-mediated immunity. Trends Mol. Med. 24:412-427
- Almudena García-Ortiz, Sales Ibiza, Noa Martín-Cofreces, Angel Ortega, Alicia Izquierdo-Alvarez, Antonio Trullo, Victor M. Victor, Enrique Calvo, Antonio Martínez-Ruiz, Jesús Vázquez, Francisco Sánchez-Madrid and Juan M. Serrador. (2017) S-nitrosylation of b-actin on Cys374 regulates PKC-q localization and activation at the immune synapse. PLOS Biology 15: e2000653
- Antonio Martínez-Ruiz, Ines M. Araujo, Alicia Izquierdo-Alvarez, Pablo Hernansanz-Agustín, Santiago Lamas, and Juan M. Serrador. (2013). Specificity in S-nitrosylation: A short-range mechanism for NO signaling? Antioxid. Redox. Sign. 19: 1220-1235.
- Díaz-Muñoz MD, Osma-García IC, Iñiguez MA, Fresno M (2013). Cyclooxygenase-2 deficiency in macrophages leads to defective p110γ PI3K signaling and impairs cell adhesion and migration. J Immunol. 191:395-406.
- Díaz-Muñoz MD, Osma-García IC, Fresno M, Iñiguez MA (2012). Involvement of PGE2 and the cAMP signalling pathway in the up-regulation of COX-2 and mPGES-1 expression in LPS-activated macrophages. Biochem J. 443:451-61.
- Díaz-Muñoz MD, Osma-García IC, Cacheiro-Llaguno C, Fresno M, Iñiguez MA (2010). Coordinated up-regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 and microsomal prostaglandin E synthase 1 transcription by nuclear factor kappa B and early growth response-1 in macrophages. Cell Signal. 22:1427-36.
- Duque J, Fresno M, Iñiguez MA. (2005). Expression and function of the nuclear factor of activated T cells in colon carcinoma cells: involvement in the regulation of cyclooxygenase-2. J Biol Chem. 280: 8686-93.
- Francesc Baixauli, Noa Martín-Cófreces, Giulia Morlino, Yolanda R. Carrasco, Carmen Calabia-Linares, Esteban Veiga, Juan M. Serrador, and Francisco Sánchez-Madrid (2011). The mitocondrial fission factor dynamin-related protein-1 modulates T cell receptor signaling at the immune synapse. EMBO J 30:1238-1250.
- Guillem-Llobat P, Íñiguez MA (2015). Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced gene expression by liver X receptor ligands in macrophages involves interference with early growth response factor 1. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 96:37-49.
- Sales Ibiza, Victor M. Victor, Irene Boscá, Ángel Ortega, Ana Urzainqui, Jose E. O’connor, Francisco Sánchez-Madrid, Juan V. Esplugues, and Juan M. Serrador (2006) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase regulates T cell receptor signalling at the immunological synapse. Immunity 24:753-765




















