Virus-Cell interaction. The ASFV model
Research summary:
African swine fever (ASF) is a devastating disease affecting both wild boar and domestic pigs. An outbreak in the Caucasus in 2007 started its spread across Russia and Eastern Europe, currently affecting Ukraine, Belarus, Poland, the Baltic States, the Czech Republic, Hungary, Moldova, Bulgaria and Romania. In August 2018 outbreaks in Belgium and China were reported, which represent dramatic extensions of the geographic distribution of ASF and further elevates the threat to the global swine industry. This situation makes imperative to improve our knowledge to make defensive tools against this important pathogen. The ASFV genome encodes many genes which are not essential for virus replication but are known to control host immune evasion, such as NFκB and the NFAT regulator A238L, the apoptosis inhibitor A224L, the viral homologous to cellular CD2, which mediates hemadsorption and AP-1 regulation, and several genes modulating the IFN synthesis in the infected cell. These genes are hypothesized to be involved in the natural attenuation of the genotype I parental ASFV NH/P68. Our group is currently spending efforts to build live attenuated vaccines (LAV) prototypes, by constructing recombinant viruses both from the naturally attenuated NH/P68 and from the virulent, presently circulating in Europe and China Armenia/07. The recombinant prototypes, lacking several of selected specific genes, have been generated mainly by using CRISPR technology and plate selection. Modified, naturally attenuated ASFV NH/P68 strain, produced in porcine alveolar macrophages (PAM) was used to vaccinate pigs that were protected against both homologous (genotype I) Lisbon 60 (L60) and heterologous Armenia/07 (genotype II). The recombinant viruses carrying specific deletions were all fully protective against parental L60 and only slightly protective against the heterologous circulating Armenia07 strain. Furthermore, our results suggested that apart from the viral skills acting to evade the immune system, lack of protection should be likely related to the cell line used to generate the vaccine; therefore, identifying a bottleneck that will compromise the safe commercial production of efficacious LAVs. In this regard, we have recently established several cell lines that can be potentially used to produce ASFV vaccines, which include COS-7 cells (only for virulent strains) and modified WSL, (a wild boar-derived lung cell line), which can be useful alternatives to the macrophage, the natural target of the infection in vivo.
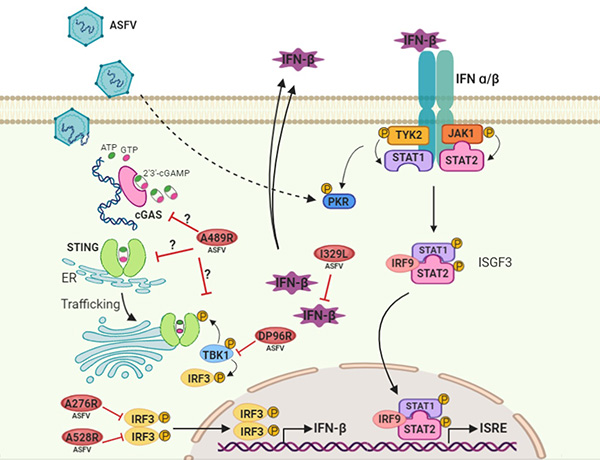
Figure 1. Simplified overview of the IFN signalling pathways putatively counteracted by ASFV, focus on the cGAS-STING and JAK/STAT pathways.
Figure 2. Recombinant ASFV-GFP generated by CRISPR-Cas9 technology isolated by plaque assay.

| Last name | Name | Laboratory | Ext.* | Professional category | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flores Simón | Cecilia | 225 | 4589 | cflores(at)cbm.csic.es | M2 |
| Gata de Benito | Julia | 225 | 4598 | Titulado Sup. Actividades Tecn. y Prof.GP1 | |
| Pérez Núñez | Daniel | 225 | 4598 | daniel_perez(at)cbm.csic.es | Doctor FC1 |
| Piredda | Roberta | 225 | 4598 | rpiredda(at)cbm.csic.es | Investigador Indef. GP1 |
| Revilla Novella | Yolanda | 225 | 4570 | yrevilla(at)cbm.csic.es | E. Investigadores Científicos de Organismos Públicos |
| Vigara Astillero | Gonzalo | 225 | 4598 | gvigara(at)cbm.csic.es | M3 Predoc.formación |
Relevant publications:
- An Update on African Swine Fever Virology. Karger A, Pérez-Núñez D, Urquiza J, Hinojar P, Alonso C, Freitas FB, Revilla Y, Le Potier MF, Montoya M. Viruses. 2019 Sep 17;11(9). pii: E864. doi: 10.3390/v11090864. Review. PMID:31533244
- Development of vaccines against African swine fever virus. Sánchez EG, Pérez-Núñez D, Revilla Y. Virus Res. 2019 May;265:150-155. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2019.03.022. Epub 2019 Mar 25. Review. PMID:30922809
- African Swine Fever Virus Armenia/07 Virulent Strain Controls Interferon Beta Production through the cGAS-STING Pathway. García-Belmonte R, Pérez-Núñez D, Pittau M, Richt JA, Revilla Y. J Virol. 2019 May 29;93(12). pii: e02298-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02298-18. Print 2019 Jun 15.PMID: 30918080
- Evaluation of a viral DNA-protein immunization strategy against African swine fever in domestic pigs. Pérez-Núñez D, Sunwoo SY, Sánchez EG, Haley N, García-Belmonte R, Nogal M, Morozov I, Madden D, Gaudreault NN, Mur L, Shivanna V, Richt JA, Revilla Y. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2019 Feb;208:34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2018.11.018. Epub 2018 Dec 21. PMID: 30712790
- DNA-Protein Vaccination Strategy Does Not Protect from Challenge with African Swine Fever Virus Armenia 2007 Strain. Sunwoo SY, Pérez-Núñez D, Morozov I, Sánchez EG, Gaudreault NN, Trujillo JD, Mur L, Nogal M, Madden D, Urbaniak K, Kim IJ, Ma W, Revilla Y, Richt JA. Vaccines (Basel). 2019 Jan 28;7(1). pii: E12. doi: 10.3390/vaccines7010012.PMID: 30696015
- African Swine Fever Virus Biology and Vaccine Approaches. Revilla Y, Pérez-Núñez D, Richt JA. Adv Virus Res. 2018;100:41-74. doi: 10.1016/bs.aivir.2017.10.002. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Review. PMID:29551143
- African swine fever virus (ASFV) protection mediated by NH/P68 and NH/P68 recombinant live-attenuated viruses. Gallardo C, Sánchez EG, Pérez-Núñez D, Nogal M, de León P, Carrascosa ÁL, Nieto R, Soler A, Arias ML, Revilla Y.Vaccine. 2018 May 3;36(19):2694-2704. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.03.040. Epub 2018 Mar 30. PMID: 9609966
- Mechanisms of Entry and Endosomal Pathway of African Swine Fever Virus. Sánchez EG, Pérez-Núñez D, Revilla Y. Vaccines (Basel). 2017 Nov 8;5(4). pii: E42. doi: 10.3390/vaccines5040042. Review. PMID: 29117102
- Approaches and Perspectives for Development of African Swine Fever Virus Vaccines. Arias M, de la Torre A, Dixon L, Gallardo C, Jori F, Laddomada A, Martins C, Parkhouse RM, Revilla Y, Rodriguez FAJ; Sanchez-Vizcaino. Vaccines (Basel). 2017 Oct 7;5(4). pii: E35. doi: 10.3390/vaccines5040035. Review.PMID: 28991171
- Characterization of the African Swine Fever Virus Decapping Enzyme during Infection. Quintas A, Pérez-Núñez D, Sánchez EG, Nogal ML, Hentze MW, Castelló A, Revilla Y. J Virol. 2017 Nov 30;91(24). pii: e00990-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00990-17. Print 2017 Dec 15. PMID: 29021398
- Phenotyping and susceptibility of established porcine cells lines to African Swine Fever Virus infection and viral production. Sánchez EG, Riera E, Nogal M, Gallardo C, Fernández P, Bello-Morales R, López-Guerrero JA, Chitko-McKown CG, Richt JA, Revilla Y. Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 4;7(1):10369. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09948-x. PMID: 28871180
Participation in R&D and Innovation projects:
- Validación de dianas farmacológicas neuroinflamatorias para el tratamiento del dolor crónico. INFLAPAIN Yolanda Revilla Novella. (CBMSO-CSIC-UAM). 01/11/2018- 04/02/2021. 245 €.
- Desarrollo de compuestos terapéuticos basados en los sitios moleculares de interacción entre la proteína viral A238L y los complejos transcripcionales que regulan la síntesis de mediadores proinflamatorios y tumorales Yolanda Revilla Novella. (Fundación Ramón Areces). 02/03/2017-01/02/2020. 110 €.
- Novel Vaccine Approaches against ASFV CEEZAD. Yolanda Revilla Novella. (CBMSO-CSIC KSU). 06/11/2014-12/03/2019. 200 €.
- Nuevas Herramientas de Diagnostico y Desarrollo de Vacunas. BIO2013-46605-R Yolanda Revilla Novella. (Centro de Biología Molecular Severo Ochoa). 02/01/2014- 31/12/2016. 140.000 €.
- Novel vaccine approaches against African Swine Fever Virus CEEZAD Funded Research. Yolanda Revilla Novella (Centro de Biología Molecular Severo Ochoa). 2014-2016. 61,5 €.
- Targeted research effort on African swine fever. ASFORCE U.E. (Seventh Framework Programme). Yolanda Revilla Novella. (Centro de Biología Molecular Severo Ochoa). 2013-2016. 225.847 €.
- Molecular mechanisms of virus-host interaction Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia (BFU2010-17794). Yolanda Revilla Novella. (Centro de Biología Molecular Severo Ochoa). 2010-2013. 120.000 €.
- Evaluating and controlling the risk of African swine fever in the EU. ASFRISK. U.E. (Seventh Framework Programme). Ángel López Carrascosa/ Yolanda Revilla Novella. (Centro de Biología Molecular Severo Ochoa). 2008-2011. 297.000 €.
- Procesos celulares modulados por virus y generación de nuevos productos antivirales. (el modelo del VPPA). Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia (BFU2007-63110). Yolanda Revilla Novella. (Centro de Biología Molecular Severo Ochoa). 2007-2010. 146.000 €.
Participation in R&D and Innovation contracts:
- Development of new tools for ASFV vaccine Laboratorios Hipra, S.A. Yolanda Revilla Novella. 14/10/2019-14/10/2023. 170.000 €.
- ASFV Vaccine Development CAHEC (Center Animal Health Emerging China). Yolanda Revilla Novella. 03/12/2018-P2Y. 210 €.
- ASFV Tet on Vaccine development Neotech CDTI. Yolanda Revilla Novella. 12/12/2017-P3Y. 134 €
- Sardinian strain ASFV vaccine development. Universitá de Sassari-CBMSO Yolanda Revilla Novella. 16/11/2017-P3Y.66 €




















