Molecular basis of Huntington's disease and other central nervous system disorders
Research summary:
We study the molecular mechanisms underlying neural diseases by generating genetic mouse models (like the HD94 Huntington’s model Cell 101:57-66 2000 cited 972 times, the Tet/GSK3 Alzheimer’s model EMBO J 20:27-39 2001 cited 870 times, or the TgCPEB4Δ4 model of idiopathic autism Nature 560:441-446 2018 cited 89 times) to validate pathogenic pathways and to test new therapeutic strategies.
Huntington’s disease (HD) is an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disease characterized by involuntary movements, psychiatric symptoms and dementia. It is caused by an expansion of the trinucleotide CAG located in the huntingtin gene. By characterizing the molecular interactions of the mutated RNA and protein, and in particular their impact on RNA binding proteins and RNA processing, we found new clues about HD and other neural disorders like X-linked dystonia parkinsonism (XDP), epilepsy, autism and schizophrenia.
For instance, by characterizing the global mis-splicing signature in HD striatum (Brain 143: 2207-19, 2020 & Brain 144:2009-23, 2021) we found an alteration of tau (the protein that accumulate inside neurons in Alzheimer’s disease). By analyzing transgenic HD mouse models with varying levels of tau we demonstrated that tau contributes to HD pathogenesis and we discovered a new histopathological hallmark (the Tau Nuclear Rods or Tau Nuclear Indentations) (Nat Med. 2014, 20:881-5 cited 195 times).
Characterizing the role of cytoplasmic polyadenylation of mRNAs by CPEBs in HD, we discovered a treatable thiamine deficiency in HD brains (Sci Transl Med. 2021 13:eabe7104) which has originated a clinical trial (https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04478734).
We also found that the majority of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) risk genes are targets of CPEB4. In fact, CPEB4 shows an isoform imbalance in individuals with autism due to mis-splicing of a neuronal specific microexon. Accordingly, mice with equivalent CPEB4 imbalance show autism-like phenotype (Nature 560:441-446, 2018) and have become a useful model of idiopathic autism.
Recently, we have also described an alteration of cytoplasmic polyadenylation in epilepsy (Brain 143: 2139-53 2020).
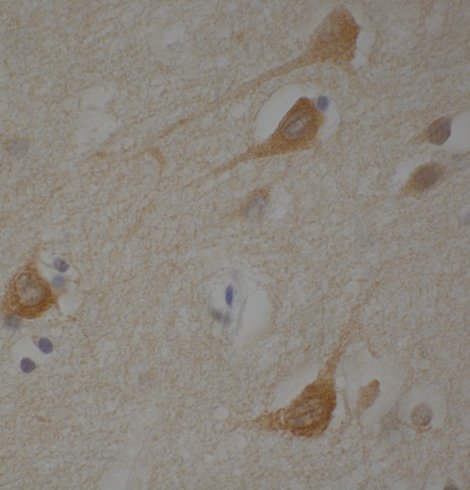
Tau Nuclear Rods (TNRs) in neurons of an HD patient.
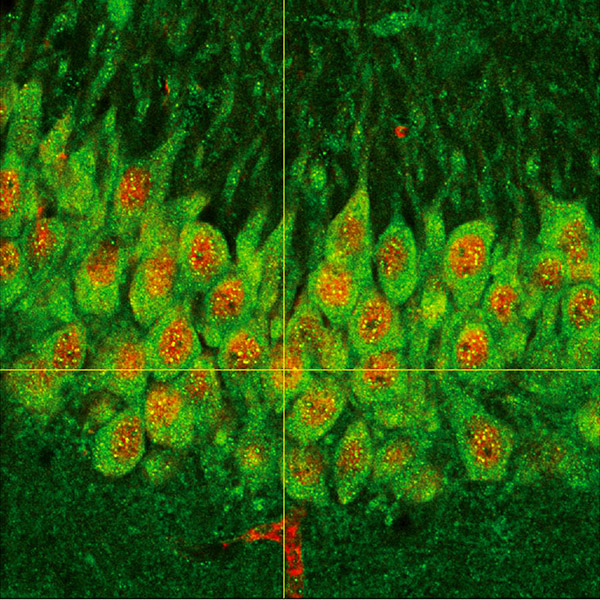
Expression of the transcription factor ATF5 in mouse hippocampal neurons.

| Last name | Name | Laboratory | Ext.* | Professional category | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arroyo García | Alejandra María | 209 | 4582 | amarroyo(at)cbm.csic.es | M3 Predoc.formación |
| Coiduras del Olmo | Marta | 209 | 4552 | Becario JAE Intro | |
| González Bermejo | María | 209 | 4452 | M3 Predoc.formación | |
| Khachatryan Boyajyan | Avetik Arsen | 209 | 4582 | Estudiante TFG | |
| Lozano Muñoz | David | 209 | 4552 | dlozano(at)cbm.csic.es | Titulado Sup. Actividades Tecn. y Prof.GP1 |
| Lucas Lozano | José Javier | 209 | 4552 | jjlucas(at)cbm.csic.es | E. Profesores de Investigación de Organismos Públicos de Investigación |
| Lucas Santamaría | Miriam | 209 | 4582 | mmlucas(at)cbm.csic.es | Contratado CIBER |
| Pose Utrilla | Julia | 209 | 4582 | jpose(at)cbm.csic.es | Titulado Superior Grado de Doctor |
| Rodríguez López | Claudia | 209 | 4582 | crodriguez(at)cbm.csic.es | M3 |
| Ruiz Blas | Irene | 209 | 4582 | M2 |
Publicaciones relevantes:
- Ollà I, Pardiñas AF, Parras A, Hernández IH, Santos-Galindo M, Picó S, Callado LF, Elorza A, Rodríguez-López C, Fernández-Miranda G, Belloc E, Walters JTR, O'Donovan MC, Méndez R, Toma C, Meana JJ, Owen MJ, Lucas JJ (2023) Pathogenic mis-splicing of CPEB4 in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2023.03.010.
- Picó S, Parras A, Santos-Galindo M, Pose-Utrilla J, Castro M, Fraga E, Hernández IH, Elorza A, Anta H, Wang N, Martí-Sánchez L, Belloc E, Garcia-Esparcia P, Garrido JJ, Ferrer I, Macías-García D, Mir P, Artuch R, Pérez B, Hernández F, Pérez-Cerdá C, Navarro P, López-Sendón JL, Iglesias T, Yang XW, Méndez R, Lucas JJ (2021) CPEB alteration and aberrant transcriptome-polyadenylation lead to a treatable SLC19A3 deficiency in Huntington’s disease. Sci. Transl. Med. DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abe7104
- Elorza A, Marquez Y, Cabrera JR, Sanchez-Trincado JL, Santos-Galindo M, Hernandez IH, Diaz-Hernandez JI, Garcia-Escudero R, Irimia M and Lucas JJ (2021) Huntington’s disease-specific mis-splicing unveils key effector genes and altered splicing factors. Brain 144:2009-23
- Hernández IH, Cabrera JR, Santos-Galindo M, Sánchez-Martín M, Domínguez V, García-Escudero R, Pérez-Álvarez MJ, Pintado B and Lucas JJ (2020) Pathogenic SREK1 decrease in Huntington’s disease lowers TAF1 mimicking X-linked dystonia parkinsonism. Brain 143:2207-19
- Parras A, de Diego-Garcia L, Alves M, Beamer E, Conte G, Jimenez-Mateos EM, Morgan J, Ollà I, Hernandez-Santana Y, Delanty N, Farrell MA, O’Brien DF, Ocampo A, Henshall DC, Méndez R, Lucas JJ* and Engel T* (2020) mRNA polyadenylation as a novel regulatory mechanism of gene expression in temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 143:2139-53
- Parras A, Anta H, Santos-Galindo M, Swarup V, Elorza A, Nieto-González JL, Picó S, Hernández IH, Díaz-Hernández JI, Belloc E, Rodolosse A, Parikshak NN, Peñagarikano O, Fernández-Chacón R, Irimia M, Navarro P, Geschwind DH, Méndez R, Lucas JJ. (2018) Autism-like phenotype and risk gene mRNA deadenylation by CPEB4 mis-splicing. Nature 560:441-6
- Hernández IH, Torres-Peraza J, Santos-Galindo M, Ramos-Morón E, Fernández-Fernández MR, Pérez-Álvarez MJ, Miranda-Vizuete A, Lucas JJ. (2017) The neuroprotective transcription factor ATF5 is decreased and sequestered into polyglutamine inclusions in Huntington's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 134:839-50
- McKinnon C, Goold R, Andre R, Devoy A, Ortega Z, Moonga J, Linehan JM, Brandner S, Lucas JJ, Collinge J and Tabrizi SJ. (2015) Prion-mediated neurodegeneration associated with early impairment ofubiquitin-proteasome system. Acta Neuropathol. 131:411-25
- Fernández-Nogales M, Cabrera JR, Santos-Galindo M, Hoozemans JJM, Ferrer I, Rozemuller AJM, Hernández F, Avila J and Lucas JJ (2014) Huntington’s disease is a four-repeat tauopathy with tau-nuclear rods. Nat Med 20, 881-5
- Torres-Peraza JF, Engel T, Martín-Ibañez R, Fernández-Fernández MR, Esgleas M, Canals JM, Henshall DC & Lucas JJ (2013) Protective neuronal induction of ATF5 in endoplasmic reticulum stress induced by status epilepticus. Brain 136:1161-76
- Gomez-Sintes R and Lucas JJ (2010) NFAT/Fas-signaling mediates apoptosis and neurological side effects of GSK-3 inhibition in a mouse model of lithium therapy. J Clin Invest 120:2432-45
- Maynard CJ, Böttcher C, Ortega Z, Smith R, Florea BI, Diaz-Hernandez M, Brundin P, Overkleeft H, Li JY, Lucas JJ & Dantuma N (2009) Accumulation of ubiquitin conjugates in a polyglutamine disease model occurs without global ubiquitin/proteasome system impairment PNAS 106:13986-91
- Gómez-Sintes R, Hernández F, Bortolozzi A, Artigas F, Avila J, Zaratin P, Gotteland J-P & Lucas JJ (2007) Neuronal apoptosis and reversible motor deficit in dominat-negative GSK-3 conditional transgenic mice. EMBO J. 26: 2743-54
- Lucas JJ, Hernández F, Gómez-Ramos P, Morán MA, Hen R, and Avila J (2001) Decreased nuclear ß-catenin, tau hyperphosphorylation and neurodegeneration in GSK-3ß conditional transgenic mice. EMBO J. 20, 27-39
- Yamamoto A*, Lucas JJ* & Hen R (2000) *These authors contributed equally to the work. Reversal of neuropathology and motor dysfunction in a conditional model of Huntingtron´s Disease. Cell 101: 57-66
Other activities:
- Part of the Networking Research Center on Neurodegenerative Diseases (CIBERNED)
- José Lucas named Member of the National Royal Academy of Pharmacy in June 2011




















